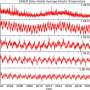
Carbon dioxide is shrinking uppermost atmosphere, prolonging life of space debris
Near Earth's surface, increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are causing temperatures to rise. But starting around 60 kilometers (37 miles) up, in the outermost layers of atmosphere called the mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT) carbon dioxide actually cools the atmosphere, causing it to shrink and contract. That cooling and contracting process has been hypothesized for over three decades. Now, new research reveals the first evidence that globally, upper atmospheric shrinking has begun.